In the dynamic landscape of modern business, the strategy of offshoring has become increasingly prevalent, reshaping the way organizations operate and manage their workforce. Offshoring, defined as the relocation of business processes or services to another country, is a strategic decision that offers a myriad of benefits and challenges. This phenomenon has gained significant traction over the past few decades, reshaping the way businesses operate and impacting economies worldwide.
In this blog we explore the concept of offshoring, its definition, benefits, and implications, with a focus on key elements such as contract labor, global payroll services, language barriers, and the role of human resources.
Let us first understand what offshoring is?
Offshoring, at its core, involves the transfer of specific business functions, such as manufacturing, IT support, or customer service, to countries with favorable economic conditions. This strategic move is often driven by factors such as cost reduction, access to specialized talent, and market expansion opportunities. Offshoring differs from outsourcing in that it typically involves the establishment of offshore subsidiaries or facilities rather than contracting third-party service providers.
Offshoring is gaining traction because of its many benefits for organizations who are looking to bring business efficiencies, want to access global talent, want to expand globally or want to cater to clients across time zones.
Here are top benefits of offshoring:
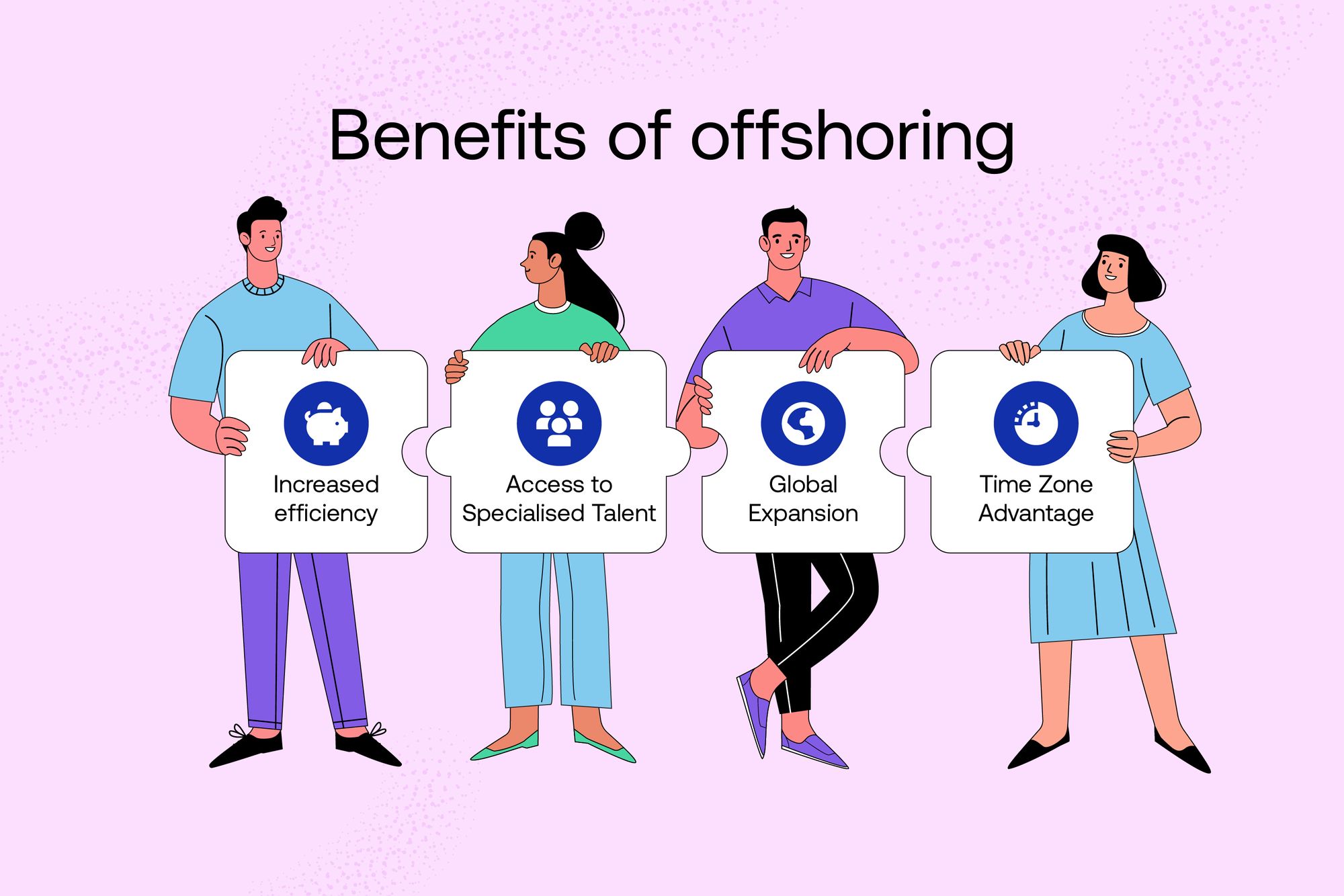
1. Increased Efficiency: Offshoring enables organizations to capitalize on lower labor costs in offshore locations, leading to significant cost savings in operations. By relocating certain functions to countries with lower wage rates and overhead expenses, organizations can achieve greater cost efficiency while maintaining or improving service quality. Offshoring can lead to increased operational efficiency and productivity. By outsourcing non-core functions to specialized service providers in other countries, companies can focus their resources and efforts on core business activities, thereby streamlining their operations and improving overall efficiency.
2. Access to Specialized Talent: Offshoring provides access to a diverse pool of skilled professionals and specialized expertise that may not be readily available domestically. Organizations can leverage the talent pool in offshore locations to fill skill gaps, drive innovation, and enhance competitiveness in the global marketplace. Offshoring allows businesses to tap into a diverse talent pool across the globe. Many developing countries have a large pool of skilled workers who are willing to work at lower wages compared to their counterparts in developed nations. This provides companies with access to specialized skills and expertise that may not be readily available domestically.
3. Global Expansion: Offshoring facilitates market expansion by establishing a presence in new geographic regions and tapping into emerging markets. By strategically positioning operations in offshore locations, organizations can gain access to new customer segments, diversify their revenue streams, and capitalize on international growth opportunities.
4. Time Zone Advantage: Offshoring to countries in different time zones can enable round-the-clock operations. This can be particularly advantageous for businesses that require continuous customer support or have tight deadlines to meet. By leveraging time zone differences, companies can ensure uninterrupted workflow and faster turnaround times.
Now that we have understood what is offshoring and its benefits, let’s also understand what all offshoring includes in its purview. If today you, as a founder, decide to offshore your business, there are quite a few changes you’ll have to make.
However, there are several agencies like Kaamwork who can help you in managing offshore workforce dynamics like:
1. Contract Labor and Contract Employees: Offshoring often involves the engagement of contract labor or contract employees to fulfill specific roles or projects in offshore locations. Contract labor arrangements offer flexibility and scalability for organizations, allowing them to adjust their workforce size and composition based on business needs. Contract employees may work on a temporary or project-based basis, providing specialized skills and expertise for defined periods. Navigating the legal and regulatory landscape of offshore operations can be daunting, with varying labor laws, tax regulations, and compliance requirements across different countries. Kaamwork offers comprehensive compliance support, ensuring that organizations remain compliant with local laws and regulations in their offshore locations. From payroll processing to tax withholding and employee benefits administration, Kaamwork takes care of the intricacies of compliance, allowing organizations to focus on their core business objectives.
2. Global Payroll Services: Managing payroll for an offshore workforce presents unique challenges related to currency exchange, tax compliance, and regulatory requirements. Global payroll services providers offer specialized solutions to streamline payroll operations across multiple countries or regions. These services ensure compliance with local tax laws, facilitate currency conversions, and provide a centralized platform for payroll processing and reporting. By outsourcing payroll operations to global service providers, organizations can mitigate compliance risks, reduce administrative burdens, and ensure timely and accurate payment of wages to offshore employees. Kaamwork provides global payroll services, streamlining payroll processing, and ensuring timely and accurate payment of wages to offshore employees. With expertise in currency management, tax withholding, and statutory reporting, Kaamwork offers a centralized platform for payroll administration, reducing administrative overhead and mitigating compliance risks for organizations.
3. Language Barriers: One of the key challenges in managing offshore operations is overcoming language barriers and cultural differences. Communication plays a critical role in effective collaboration and coordination across global teams. Organizations must invest in language training and cross-cultural awareness programs to foster a collaborative work environment and minimize misunderstandings Kaamwork offers language training and cross-cultural awareness programs to bridge the gap between offshore employees and their counterparts in the organization. By fostering a culture of inclusivity and understanding, Kaamwork helps organizations overcome language barriers and maximize the productivity and cohesion of their offshore teams.
4. Finding the Right Talent: One of the key advantages of offshoring is its scalability and flexibility , allowing organizations to quickly adapt to changing business needs and market demands. However hiring, retaining, and maintaining the right talent globally is always a challenge. Kaamwork offers flexible staffing solutions, enabling organizations to scale their offshore teams up or down as needed without the burden of long-term commitments. Whether it's ramping up resources for a new project or adjusting team size based on seasonal fluctuations, Kaamwork provides agility and responsiveness to support organizations' evolving requirements.
5. Quick decision making: Beyond talent acquisition and operational support, Kaamwork offers strategic consulting services to help organizations maximize the benefits of offshoring. From market research and location analysis to risk assessment and performance optimization, Kaamwork collaborates with clients to develop tailored offshoring strategies aligned with their business objectives. By leveraging industry insights, best practices, and proven methodologies, Kaamwork empowers organizations to make informed decisions and achieve sustainable growth through offshoring.
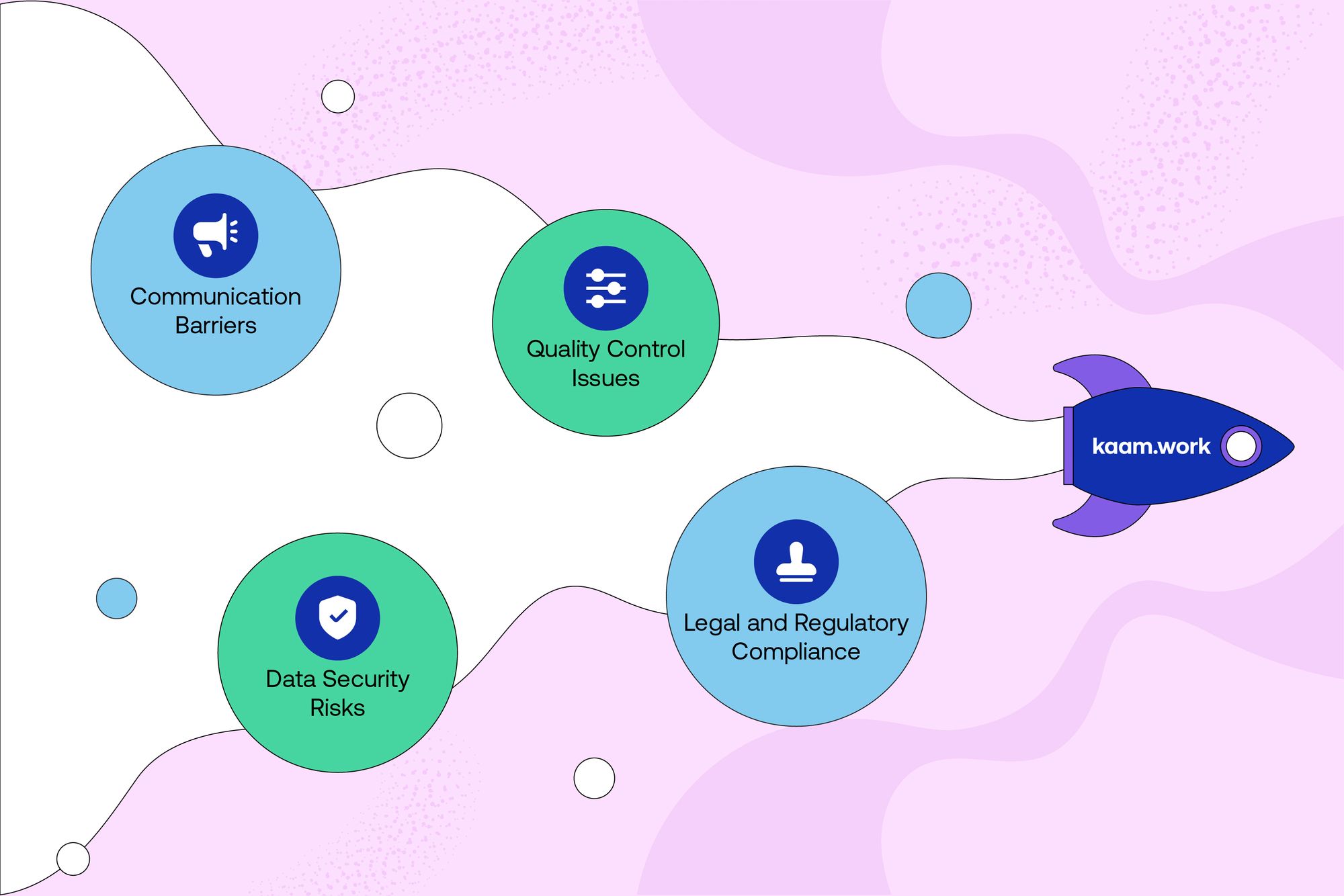
Apart from the above strategic advantages of Kaamwork there are several other challenges in offshoring which Kaamwork can help with:
1. Communication Barriers: Offshoring often involves working with teams located in different geographical locations, which can pose challenges in terms of communication. Language barriers, cultural differences, and varying work styles can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and inefficiencies if not managed effectively.
2. Quality Control Issues: Maintaining consistent quality standards across geographically dispersed teams can be a major challenge in offshoring. Differences in processes, infrastructure, and workforce capabilities may impact the quality of products or services delivered, potentially leading to customer dissatisfaction and reputational damage.
3. Data Security Risks: Offshoring involves sharing sensitive business information and data with external partners or service providers located overseas. This poses inherent risks related to data security, confidentiality, and intellectual property protection. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and compliance with relevant regulations is essential to mitigate these risks.
4. Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Offshoring activities are subject to a complex landscape of legal and regulatory requirements, both domestically and internationally. Issues such as tax implications, employment laws, and intellectual property rights can vary significantly from one country to another, posing compliance challenges for companies engaged in offshoring.
Offshoring presents both opportunities and challenges for organizations seeking to optimize their global workforce strategy. By leveraging the benefits of offshoring, such as cost efficiency, access to talent, and market expansion, organizations can gain a competitive edge in today's interconnected world. However, managing offshore operations requires careful planning, effective resource allocation, and a proactive approach to addressing key considerations such as contract labor, global payroll services, language barriers, and human resources management.
Successful offshoring initiatives require a holistic approach that integrates business objectives, regulatory compliance, and talent management practices. By understanding the nuances of offshoring and implementing best practices in workforce management, organizations can navigate the complexities of the global marketplace and drive sustainable growth and success in the long term.
FAQs:
1. What is offshoring?
Offshoring refers to the practice of relocating business processes, services, or operations to another country, typically to leverage cost advantages, access specialized talent, or expand into new markets.
2. What are the benefits of offshoring?
Offshoring offers several benefits, including cost savings, access to a global talent pool, scalability, flexibility, market expansion opportunities, and increased competitiveness.
3. What are the key considerations before offshoring?
Organizations should consider factors such as cultural compatibility, language proficiency, regulatory compliance, security risks, intellectual property protection, and geopolitical stability before embarking on offshoring initiatives.
4. What types of business processes are suitable for offshoring?
Various business processes can be offshored, including IT services, software development, customer support, back-office operations, manufacturing, finance and accounting, human resources, and research and development.
5. How do i choose the right offshore location?
Selecting the right offshore location involves evaluating factors such as labor costs, skill availability, infrastructure, language proficiency, cultural affinity, political stability, regulatory environment, time zone differences, and economic indicators.
6. What are the risks associated with offshoring?
Risks associated with offshoring include language and cultural barriers, quality control issues, data security risks, compliance challenges, legal and regulatory uncertainties, geopolitical risks, and the potential for negative public perception.
7. How can i mitigate risks in offshoring?
Mitigating risks in offshoring involves conducting thorough due diligence, implementing robust governance structures, ensuring compliance with local regulations, establishing clear communication channels, fostering cultural awareness, implementing cybersecurity measures, and maintaining transparency and accountability throughout the offshoring process.
8. What are the cost implications of offshoring?
While offshoring can lead to significant cost savings in labor and operational expenses, organizations should consider factors such as initial setup costs, ongoing maintenance costs, currency fluctuations, tax implications, and the total cost of ownership when evaluating the financial impact of offshoring.
9. How can I ensure effective communication and collaboration with offshore teams?
Effective communication and collaboration with offshore teams require clear communication channels, regular updates, cultural sensitivity, language training, the use of collaboration tools and technologies, establishing performance metrics, and fostering a collaborative work culture across geographically dispersed teams.
10. What are some best practices for offshoring?
Best practices for offshoring success include conducting comprehensive risk assessments, developing a robust offshoring strategy, selecting the right offshore partners, investing in talent development and training, maintaining open and transparent communication, monitoring performance metrics, adapting to changing market conditions, and continuously refining offshoring processes to achieve desired outcomes.

